Creating Monitoring Account First
If you are planning on using our newer monitoring services “monitor.jemrf.com”. It is recommended that you create your Monitoring Account first if you don’t have one, because in the Step of the WiFi Setup Details, you will need to know your monitoring account token. If you do not have a JemRF Monitoring Service account, the sign-up instructions to create an account are at: Create account and create a Token.
- For the legacy service, if you already have a PEP Token, you can use it on the newer JemRF Monitor service.
Setup Details
To reach the configuration page for the WiFi IoT Sensor, you can use any device that supports WiFi and an internet browser. In this example, we will use a desktop computer.
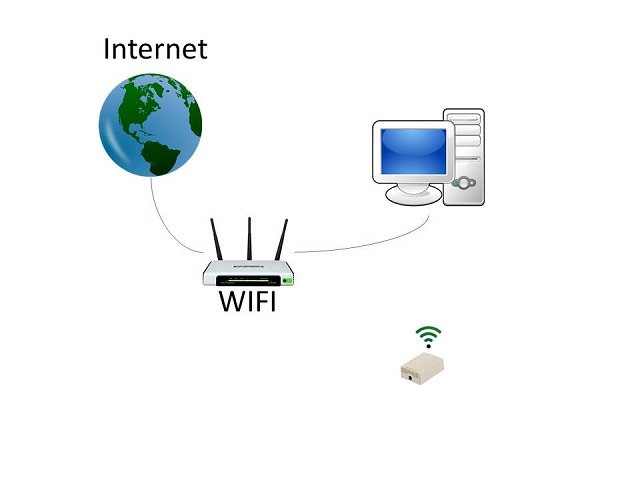
To make setup easy, the WiFi Sensor has its own Access Point.
Step 1: Connect to WiFi
The first step is to connect your smart device to the WiFi Sensor. Power up the WiFi Sensor and, using your computer (or smart device), look for a WiFi Name that starts with JEM followed by some numbers. These numbers are the unique ID of your device. Connect to the device using the default password:
Password: Jemrf32s
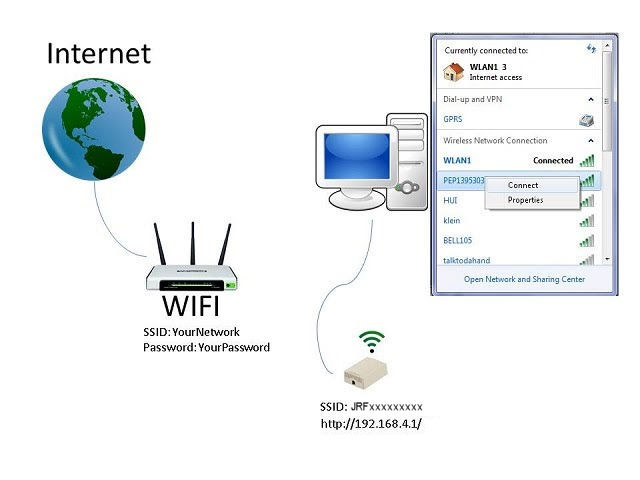
Step 2: Configure SSID and Password
Now open up a browser and navigate to http://192.168.4.1/.
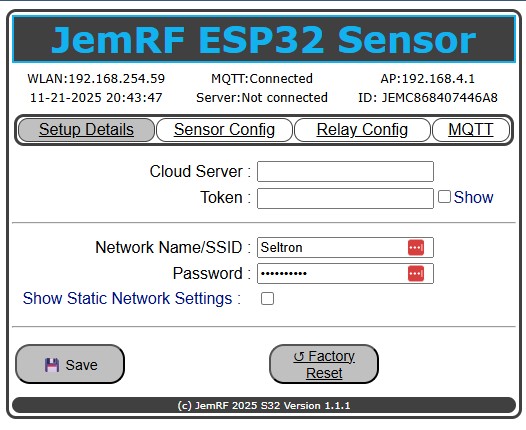
From here, you configure your WiFi Settings.
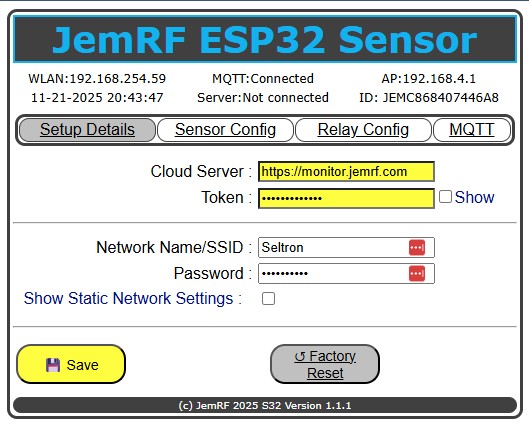
Note: Changes made but not saved are flagged in Yellow so you know they have not been saved.
Wait a few moments for the WiFi Sensor to connect to the WiFi router. Click on the “Setup Details” menu option to refresh the screen. Once connected, you will see the WLAN: IP address given to the Wireless Sensor, as shown in the following image. The example below shows 192.168.254.59; yours will be different. What’s important is that your gateway is now connected to the Internet.

Step 3: Connect to Monitoring Server
You can now switch your laptop or phone from the device’s WiFi to your home WiFi Network. If you want to use our monitoring services, “monitor.jemrf.com” is our newer service, focused on monitoring with custom tolerance settings to trigger notifications that help alert you when there is a problem. The next step is to connect your gateway to our services, allowing you to monitor devices and receive alerts. Both of our online services have a free tier. You are welcome to visit each to see which one meets your needs, and you can sign up for both (only one will be active at a time). Both use a token to link your device to your account.
Monitor.JemRF.com
If you want to use our monitoring services and do not have a JemRF Monitoring Service account, the sign-up instructions to create an account on JemRF Monitoring are available at: Create account and create a Token.
- For the legacy service, if you already have a PEP Token, you can use it on the newer JemRF Monitor service.
Step 4: Final Sensor Settings
With your Sensor now online (it has a WLAN number), you can stay on your home WiFi Network and point your browser to the WLAN address of the gateway. In the example picture above, the 192.168.254.59 would be the WLAN address for my Sensor; your address will change. Go to http://WLAN (example http://192.168.254.59).
Server
On the WiFi Sensor Setup Details page, the Server setting is monitor.jemrf.com.

Token
Using your account on monitor.jemrf.com, after you log in, click on your name in the upper right-hand corner; a dropdown menu will appear. Select Account and then click on the Edit Token button.
- If you have a PrivateEyePi token already, you can paste it in the token field and click the Accept Token to validate that it is unique and Save. Now the same token works for both servers.
- If you do not have a PrivateEyePi Token, click Generate Sensor ID and it will create a token for you.
Click Accept Token to validate that it is unique, and then save.
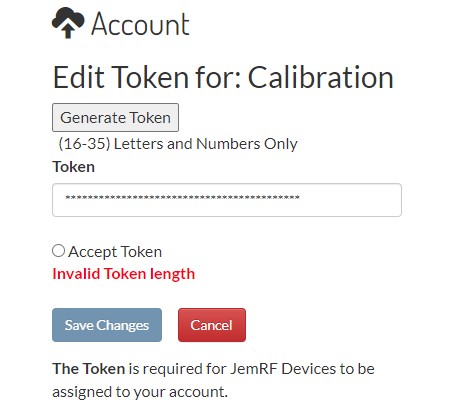
Return to the Sensor WiFi and go back to 192.168.4.1 and copy and paste the Token into the Token field as shown in the below diagram:
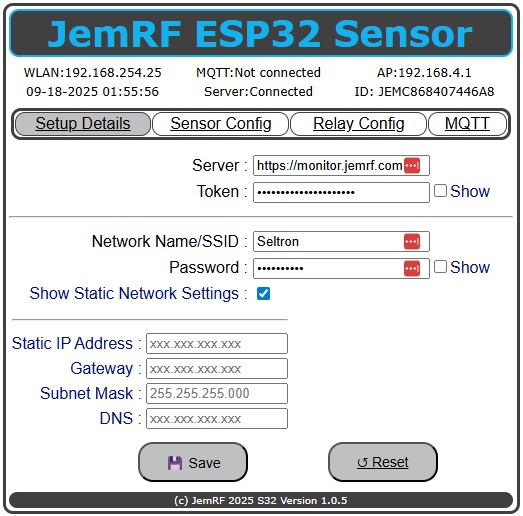
Clicking “Save” will connect the WiFi Sensor to the server. After a few moments, click on the “Setup Details” tab to refresh the screen. You will see “Server: Connected” as shown in the image above.
Once connected, the Wireless Sensor will begin forwarding its data to the monitoring server.
Manual Network Settings
The normal process for the JemRF ESP32 Sensor is the automated network request to the local router or name server using DHCP.
If needed, when checked, the options to set the network values manually are presented as show in image above.
Static IP Address
Enter the IP Address you wish to allocate to the sensor. This is useful if you are polling the device from another computer and do not want the IP Address to ever change.
Gateway, Subnet & DNS
These settings are mandatory if you want to set a static IP address. If you do not know the subnet mask and gateway of your router, you can easily get it as follows:
Windows - Open a command prompt window and type ipconfig, then page up and look for Subnet Mask and Gateway
Linux - Open a terminal session and type netstat -nr. This will give you the Gateway. Now type ifconfig, and look for the Mask.