JemRF WiFi Wireless Gateway and WiFi Sensor MQTT Options
The JemRF ESP32 WiFi Sensor has a built-in MQTT Client. It supports the same MQTT features as the Smart Gateway and WiFi Gateway. They can all send data to the Monitoring Server, which will store and display the readings on the user’s Dashboard. They can also connect to a MQTT Broker and publish the sensor readings. It can do both at the same time, or just send to the Server or the Broker. You can now use tools like Node-Red to build your own monitoring displays.
The settings for publishing sensor readings to an MQTT broker are configured on the MQTT Detail Tab, as shown in Figure 1.
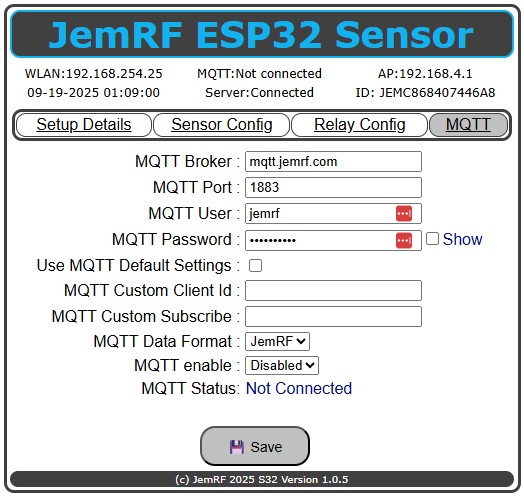 Figure 1 MQTT Details Setup.
Figure 1 MQTT Details Setup.
Getting Started
Click the MQTT tab and enter the MQTT Broker, in my case, my local server, and the MQTT port. For me, the standard MQTT port is used. Next is the optional Username and Password.
Like the JemRF Gateways, the ESP32 WiFi Sensor comes preset to Port 1883 and is configured to use the JemRF Broker. The default username is jemrf, and the default password is mqtt4jemrf. If you want a private account, contact sales @ jemrf.com. The JemRF WiFi Sensor can also make a Secure Connection. If the port numbers are 8000 or higher, the Sensor will attempt to make a Secure and Trusted Connection. If the Secure and Trusted fails, it will try a Secure and UnTrusted. Untrusted is caused when the site Certificate is not current or cannot be validated. A typical Example is using a self-signed certificate. A Secure, encrypted connection is made, but because the certificate cannot be validated, it is flagged as Untrusted. As shown in Figure 2.
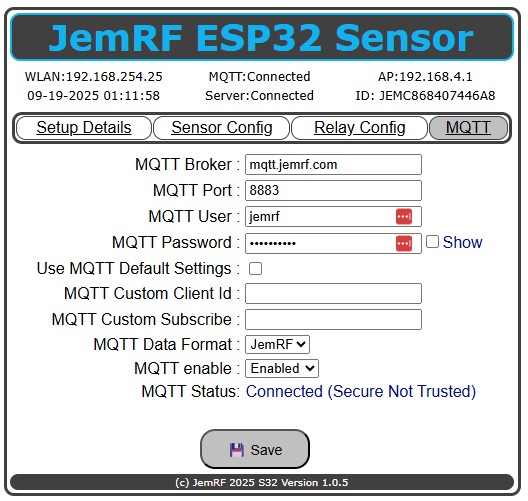 Figure 2, MQTT Connected, encrypted, but the server is not Trusted
Figure 2, MQTT Connected, encrypted, but the server is not Trusted
Publishing Format
Using the MQTT standard protocol, the Gateway will publish data to the broker using the subscription that is the combination of the Gateway Name and the sensor message. -Subscription Using the Gateway shown in Figure 1, the Gateway name is JRF03516124. Using the sensor shown in Figure 2
MQTT Formats
JemRF
This is our original format designed to support the RF sensors with the WiFi Wireless Gateway. It is now also used by the WiFi Sensor./ All messages are limited to each sensor resulting in a discrete MQTT message for each sensor. The Temperature and Humidity sensor is a single sensor so messages include both temperature and humidity in one message. All other sensors are discrete readings.
The Gateway or the WiFi Sensor default topic is: [JEM {Gateway Id}] or [PEP {PEP Id}]/
MQTT Payloads
[JemRF ID]
-
If Temperature Sensor Only
-
- [Sensor Id]
-
-
- TMPA = 56.07
-
- If Temperature & Humidity Sensor
-
- [Sensor Id] (Note for the dual sensor, the Sensor Id is the PEP Id)
-
-
- TMPA =66.23
-
-
-
- HUMD = 54.2
-
MQTT JSON
This format is a generic format and compatible with Home Assistant servers.
The default topic is: [Sensor Id]/
With Payload for temperature only (Gateway or Sensor) with readings set to Fahrenheit.
[probe id] = [{“temperature”:”78.4”},{“unit_of_measurement”:”F”}]
.. For WiFi Sensors with multiple probes, the above format is repeated for each probe.
Sensor With Payload for Temperature & Humidity sensor:
[probe id] = [[{“temperature”:”80.42”,”unit_of_measurement”:”F”}],[{“humidity”:”53.10”,”unit_of_measurement”:”%”}]]
Relau Payload
The relay state is 0 for Off and 1 for On.
Example Relay message
[{“relay2”:”0”,”unit_of_measurement”:”State”}]