The following diagram describes how communication works between the micro-controller (MCU) and Gateway.
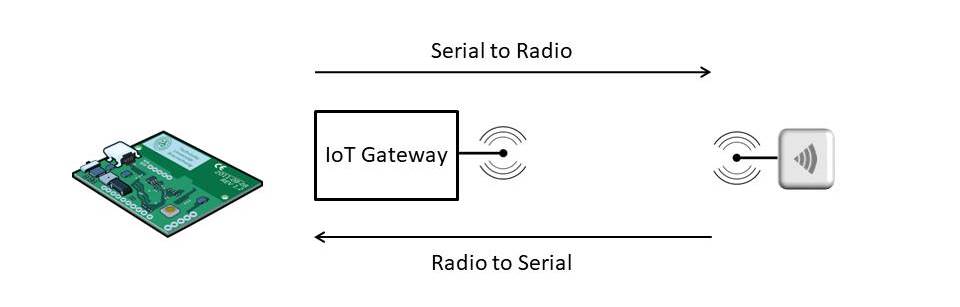
Messages are sent by the MCU to the IoT Gateway via serial and automatically transferred to radio waves that can be received by any other JemRF radio device. Conversely a sensor node can transmit messages which are received by the IoT Gateway and converted to serial input to the MCU.
There are two types of messages:
-
Command. A command is a message addressed to a specific sensor. The receiving device processes the command and provides a response back to the sender. For example the MCU may want to request a sensor reading from node 55. When node 55 receives a command for requesting a sensor reading then it takes a reading from the sensor (e.g. temperature sensor) and transmits the reading. The MCU waits for the reading to be received. This is called a “request/reply” message model. Commands are very powerful and can be used to configure a sensor or tell it to take some action. The ability to configure sensors over the air is a very important feature of IoT devices because it allows you to quickly send messages to many sensors without needing to retrieve them and connect them physically to the MCU in order to configure.
-
Sensor data. Sensors typically transmit data based on an interval (e.g. a temperature reading is sent every 5 minutes), or an event (e.g. a door was opened or motion was detected) occurs and sensor data is transmitted. The IoT Gateway listens for sensor data all the time and is able to process it as it comes in. This is called a broadcast or “fire-and-forget” message model. The sensor transmitting the data does not need to establish a handshake with the receiver as it does with the request reply model above.
In the code examples we will delve more deeply into the implementation of these two messaging models. Each have pro’s and con’s. For example the the request/reply model is used for guaranteed messaging where you want a certain degree of reliability between the gateway and the node. The broadcast model is best suited to battery powered sensors that will sleep in between transmissions to conserve battery power.